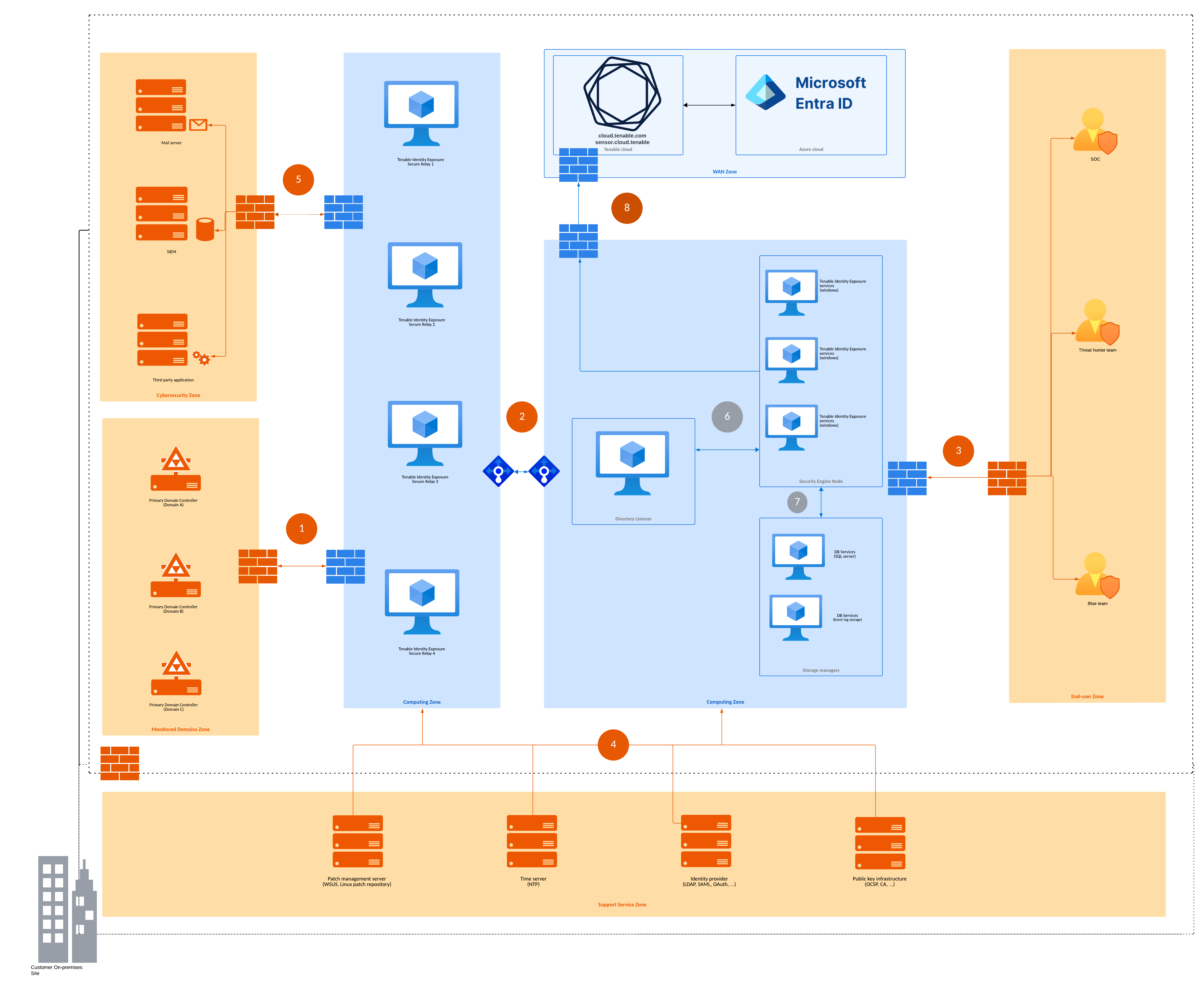
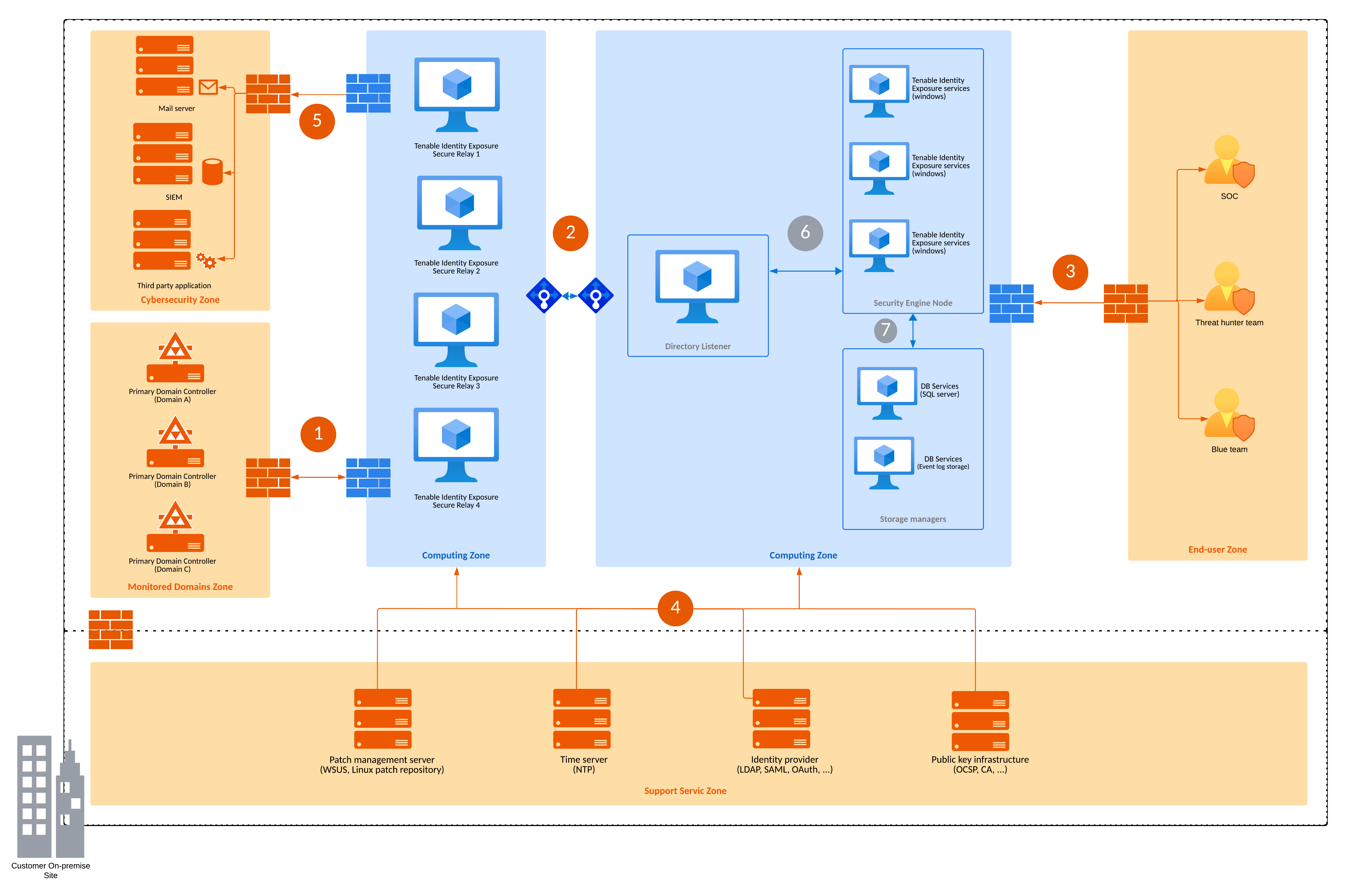
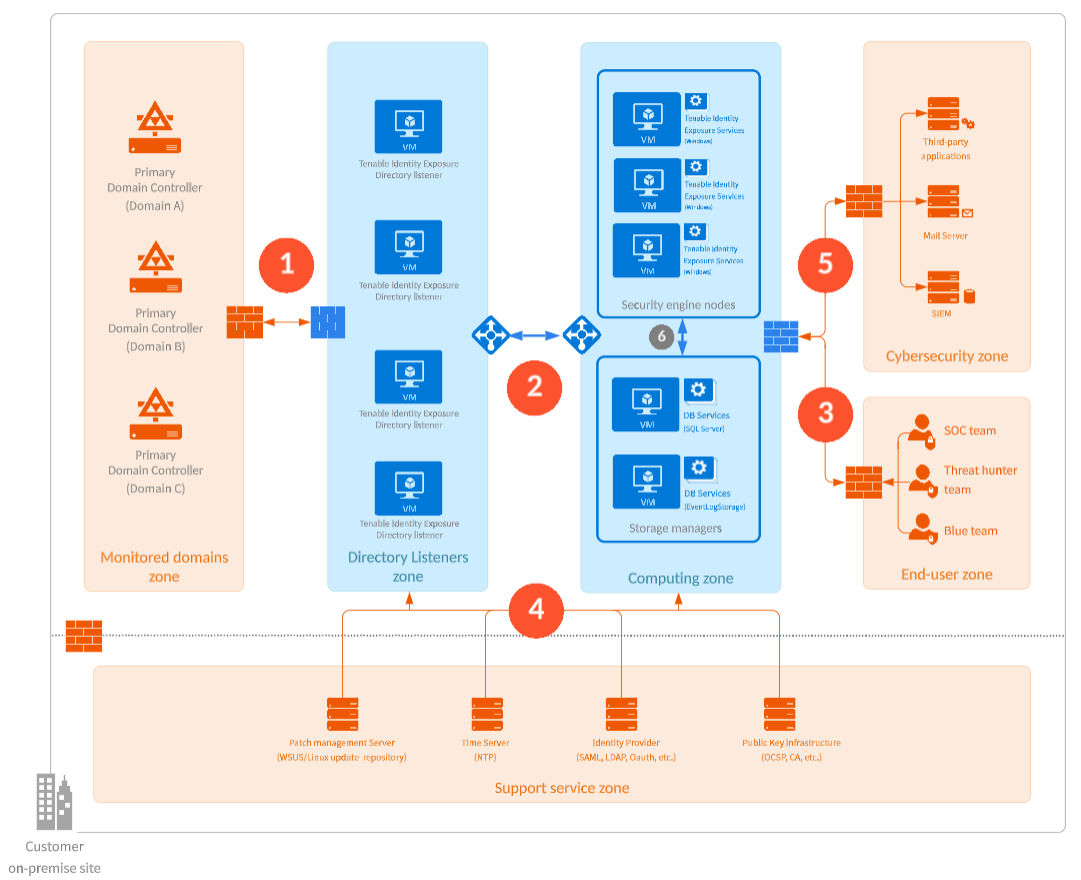
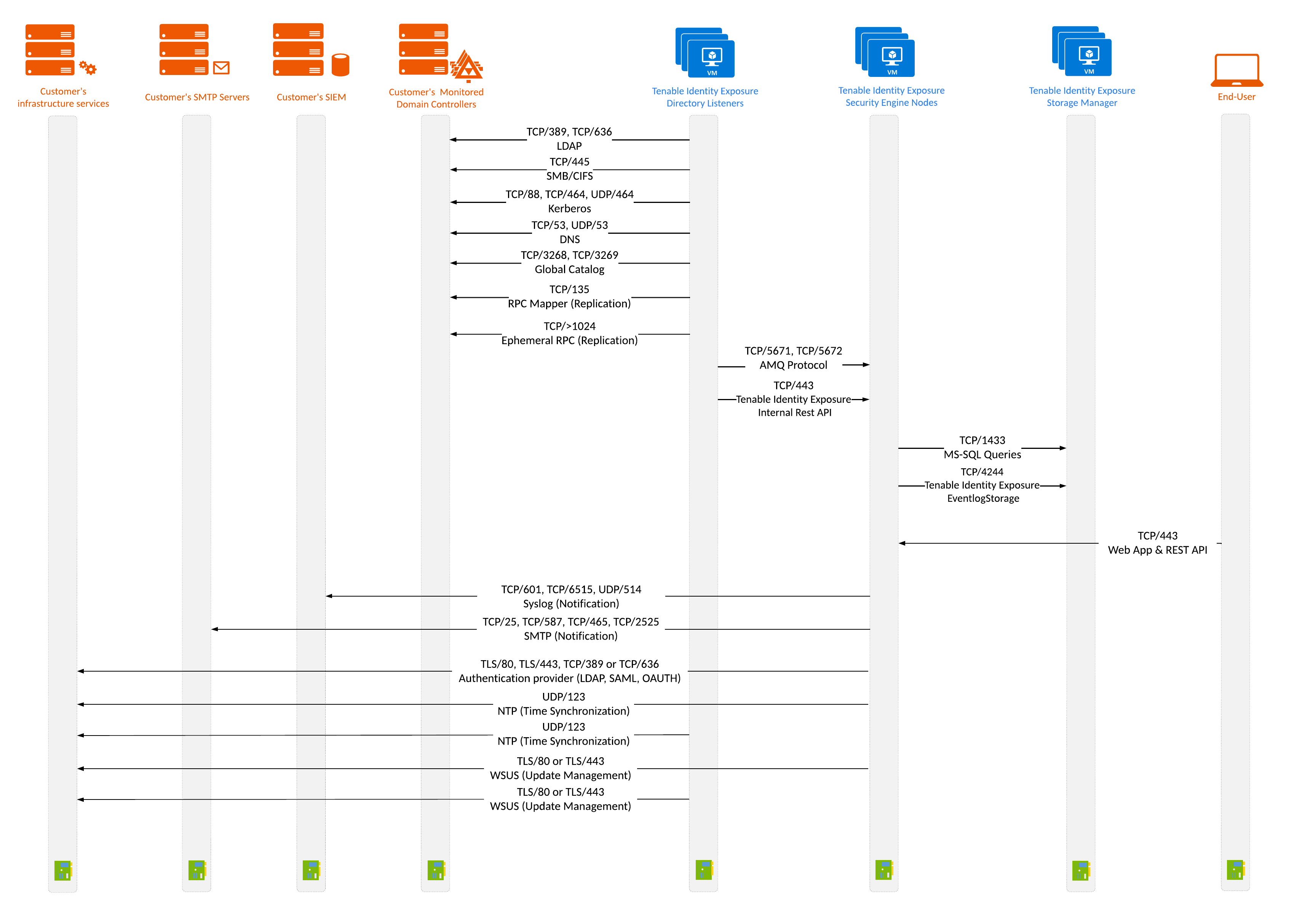
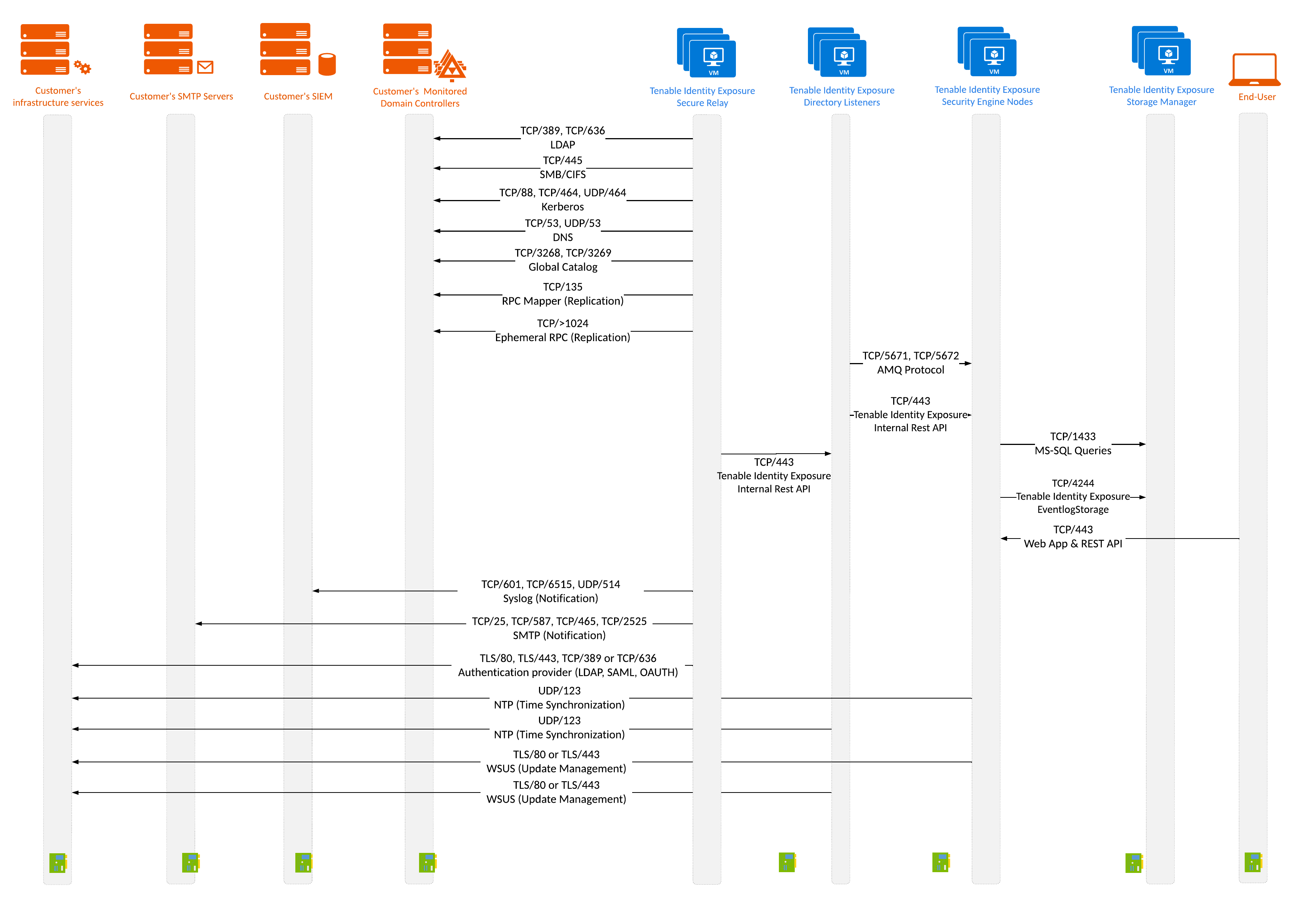
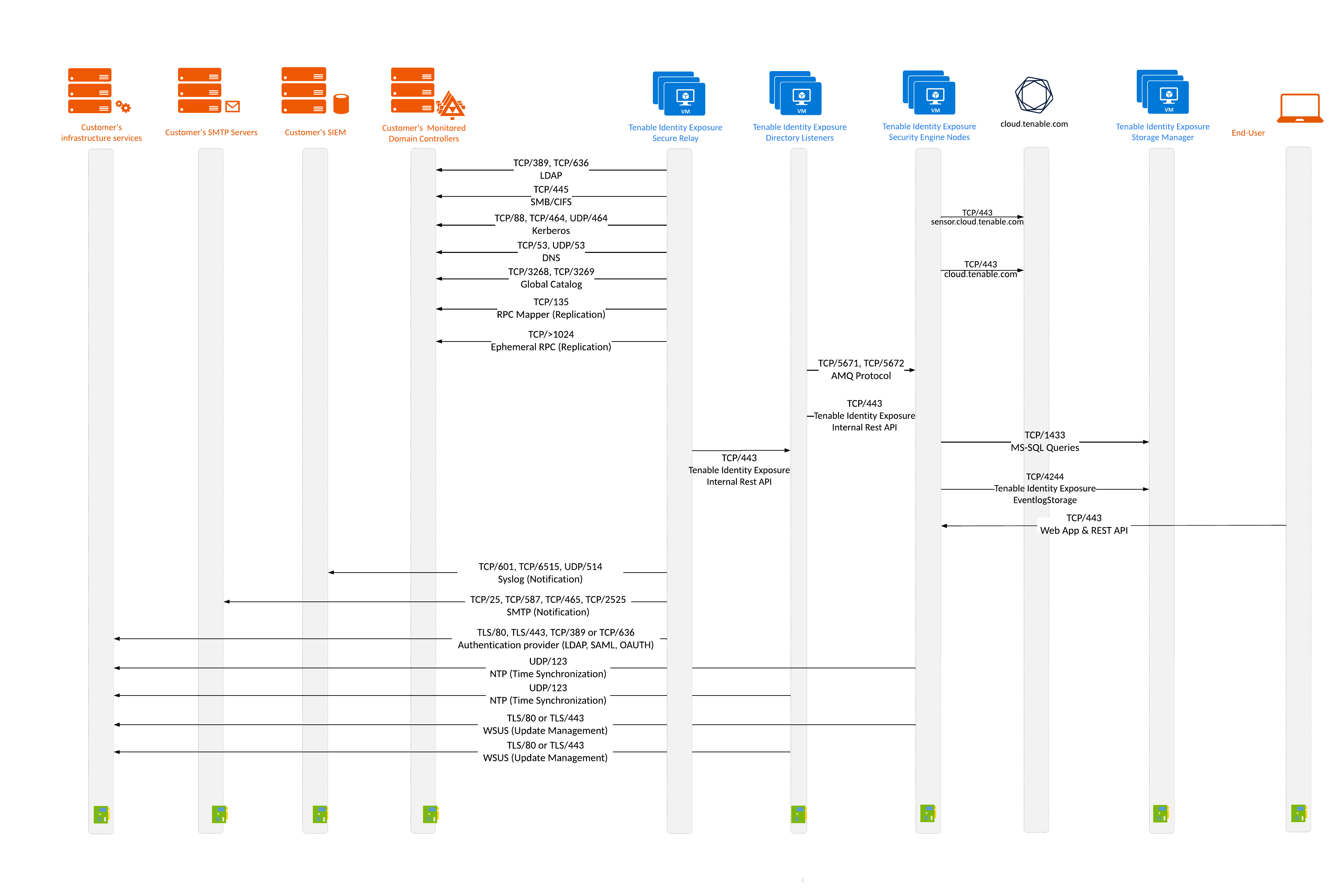
Network Flow Matrix
To do security monitoring, Tenable Identity Exposure must communicate with the Primary Domain Controller emulator (PDCe) of each domain. You must open network ports and transport protocols on each PDCe to ensure efficient monitoring.
In addition to these network flows, you must consider other network flows, such as:
-
Access to the end-user services.
-
The network flows between Tenable Identity Exposure services.
-
The network flows from the support services that Tenable Identity Exposure uses, such as the update management infrastructure and the network time protocol.
The following network matrix diagram gives more details about the different services involved.
Required Protocols
Based on this diagram, the following table describes each required protocol and port that Tenable Identity Exposure uses.
|
Network Flows |
From | To |
Tenable Identity Exposure’s Usage |
Type of Traffic |
Protocol and Port |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tenable Identity Exposure’s Secure Relay(s) | Domain controllers |
Directory, Replication, User and Computer Authentication, Group Policy, Trusts |
LDAP/LDAPS |
TCP/389 and TCP/636 ICMP/echo-request ICMP/echo-response |
|
Replication, User and Computer Authentication, Group Policy, Trusts |
SMB, CIFS, SMB2, DFSN, LSARPC, NbtSS, NetLogonR, SamR, SrvSvc |
TCP/445 |
|||
|
User and Computer Authentication, Forest Level Trusts |
Kerberos |
TCP/88, TCP/464 and UDP/464 |
|||
|
User and Computer Authentication, Name Resolution, Trusts |
DNS |
UDP/53 and TCP/53 |
|||
|
Replication, User and Computer Authentication, Group Policy, Trusts |
RPC, DCOM, EPM, DRSUAPI, NetLogonR, SamR, FRS |
TCP Dynamic (49152–65535) Note: Starting with Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, the default dynamic port range is 49152–65535. This is a change from earlier versions that used ports 1025–5000.
|
|||
|
Directory, Replication, User and Computer Authentication, Group Policy, Trusts |
Global Catalog |
TCP/3268 and TCP/3269 |
|||
|
Replication |
RPC Endpoint Mapper |
TCP/135 |
|||
| 2. | Tenable Identity Exposure’s Secure Relay(s) | Tenable Identity Exposure’s Directory Listener |
Tenable Identity Exposure’s internal API flows |
HTTPS |
TCP/443 |
| Automatic updates | HTTP | TCP/5049 | |||
|
3. |
End users | Tenable Identity Exposure’s Security engine nodes |
Tenable Identity Exposure’s end-user services (Web portal, REST API, etc.) |
HTTPS |
TCP/443 |
| 4. | Tenable Identity Exposure | Support services |
Time synchronization |
NTP |
UDP/123 |
|
Update infrastructure (for example WSUS or SCCM) |
HTTP/HTTPS |
TCP/80 or TCP/443 |
|||
|
PKI infrastructure |
HTTP/HTTPS |
TCP/80 or TCP/443 |
|||
|
Identity provider SAML server |
HTTPS |
TCP/443 |
|||
|
Identity provider LDAP |
LDAP/LDAPS |
TCP/389 and TCP/636 |
|||
|
Identity provider OAuth |
HTTPS |
TCP/443 |
Additional Flows
In addition to the Active Directory protocols, certain Tenable Identity Exposure configurations require additional flows. You must open these protocols and ports between Tenable Identity Exposure and the targeted service.
|
Network flows |
From | To |
Tenable Identity Exposure’s Usage (optional) |
Type of Traffic |
Protocol and Port |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5. | Tenable Identity Exposure’s Secure Relay(s) | Cybersecurity services |
Email notifications |
SMTP |
TCP/25, TCP/587, TCP/465, TCP/2525, TCP/25025
|
|
Syslog notifications |
Syslog |
TCP/601, TCP/6515, UDP/514 (depending on the event log server’s configuration) |
|||
| Tenable REST API | HTTP/TLS | TCP/443 | |||
| Domain controllers | Privileged Analysis | RPC dynamic ports | TCP/49152-65535, UDP/49152-65535 |
Internal Ports
If you split the Security Engine Nodes and the Storage Managers into two different subnets, Tenable Identity Exposure requires access to the following ports.
|
Network flows |
From | To |
Tenable Identity Exposure’s Usage |
Type of Traffic |
Protocol and Port |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6. | Tenable Identity Exposure’s Security Engine Nodes | Tenable Identity Exposure’s Storage Managers |
MS SQL Server database access |
MS SQL queries |
TCP/1433 |
| EventLogStorage database access | EventLogStorage queries | TCP/4244 | |||
| 6. | Tenable Identity Exposure's Directory Listener | Tenable Identity Exposure’s Security Engine Nodes |
Tenable Identity Exposure’s communication bus |
Advanced Message Queuing Protocol | TCP/5671 and TCP/5672 |
| Tenable Identity Exposure’s internal API flows | HTTP/HTTPS | TCP/80 or TCP/443 | |||
| 7. | Tenable Identity Exposure’s Security Engine Nodes | Tenable Identity Exposure’s Storage Managers |
MS SQL Server database access |
MS SQL queries |
TCP/1433 |
| EventLogStorage database access | EventLogStorage queries | TCP/4244 | |||
| 8. | Tenable Identity Exposure’s Security Engine Nodes |
Tenable Cloud
|
Tenable Identity Exposure Cloud service | HTTPS | TCP /443 |
Support Services
Support services are often highly vendor or configuration-specific. For example, the WSUS service listens by default on port TCP/8530 for its 6.2 version and higher, but on TCP/80 for other versions. You can reconfigure this port to any another port.
Network Address Translation (NAT) support
Tenable Identity Exposure initiates all network connections, except those from end users. You can use network address translation (NAT) to connect to Tenable Identity Exposure through network interconnection.